Talkshow Goodlife Insomnia on Behavioral Disorders

Insomnia in Behavioral Disorders
Dr. Fery Luvita Sari, M.Sc, Sp.N
Faculty of Medicine Universitas Islam Indonesia,
Yogyakarta Bhayangkara Hospital, Yogyakarta Griya Mahardhika Hospital
Definition of insomnia:
Insomnia is a sleep disorder condition in which a person has difficulty falling asleep/sleep-onset insomnia or difficulty maintaining sleepsleep maintenance insomnia, despite having the opportunity to sleep, the condition is ready to sleep and have time to sleep. A person often wakes up repeatedly, wakes up too early and finds it difficult to fall asleep again.
This condition causes a person's sleep to be short and inadequate, easily disturbed, poor quality, not feeling refreshed when he wakes up, uncomfortable, and does not have a restorative effect.
Insomnia symptoms:
- Sleep latency >30 minutes
- Waking time after sleep onset >30 minutes
- Sleep efficiency < 85%
- Total sleep time/total sleep time < 6-6,5 hours
- These complaints occur at least 3 days a week
Epidemiology :
1/3 of the adult population complains of insomnia, mostly the elderly, certain economic status, workers with a rotation/shift system, psychological problems, more women, alcohol/drug users, patients in hospitals or dormitories, medical disorders/neurological diseases such as chronic pain, hypertension, diabetes
Insomnia effect:
- Fatigue appears
- Decreased energy and motivation
- Cognitive impairment (concentration, memory, reaction, decision making)
- Performance degradation
- Decreased productivity
- Mood changer
- Decreased quality of life
Risk :
Causes an increased risk of accidents when driving
Drug abuse
Having a psychiatric disorder (major depression, anxiety)
Classification :
(International Classification of Sleep Disorders/ICSD)
Reason :
Disruption of circadian rhythms of sleep and wake cycles, high metabolic rate, higher EEG activity
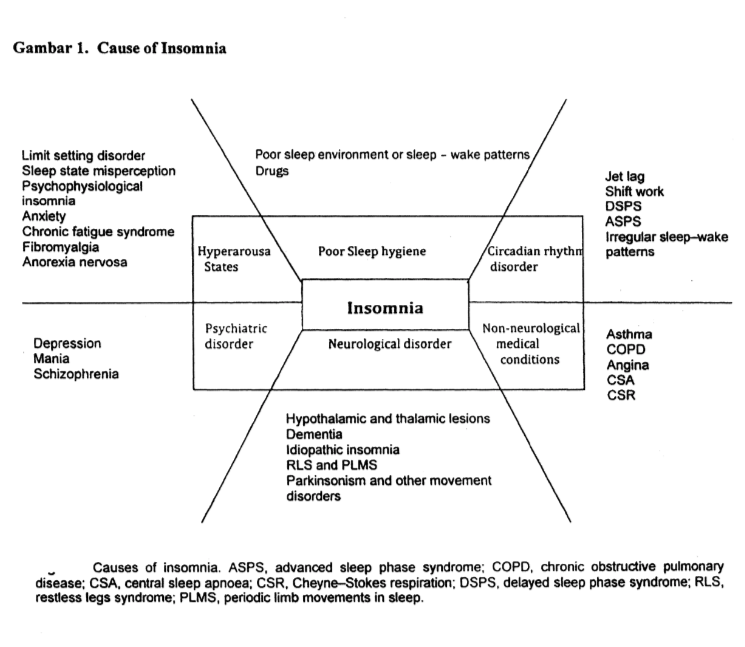
One of the causes of chronic insomnia is behavioral disorders or insomnia related to patient behavior that causes wakefulness and is not conducive to sleep
- Sleep hygiene bad habits such as excessive caffeine consumption, smoking, strenuous exercise at night, mentally stimulating activities near bedtime, using the bedroom to do chores, watching television
- Limit-setting sleep disorder often found in children who refuse when asked to sleep, the condition recurs and causes them to go to bed late at night.
- Sleep-onset association disorder when a person cannot start sleeping if he does not find an item he wants
- Nocturnal eating (drinking) syndrome i.e. the habit of eating/drinking at night.
Inspection :
- Insomnia screening
- Psychological screening
- Interview with sleeping partner
- MSLT/ Multiple sleep latency tests
- PSG/Polysomnography
Sleep efficiency, sleep latency, frequency of awakenings, sleep quality, sleep duration, total time
Handling:
Nonpharmacology
- Sleep hygiene
- Use the bed only for sleeping
- Wake up every day at a fixed time, including weekends
- Avoid lingering in bed if there is no need
- Avoid taking too many naps
- Stop the habit of alcohol, nicotine, caffeine
- Do not eat heavy before going to bed at night
- Keep the bedroom space in a comfortable condition (temperature, ventilation, noise, lighting)
- Light therapy

- Behavioral therapy
- Relaxation technique
- Stimulation control
- Temporal control
- cognitive therapy
- Sleep restriction
- Paradoxical intentions
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)/multimodality therapy
Pharmacology
- Hypnotic drugs (benzodiazepines, antidepressants, melatonin, histamine antagonists)

